Power Query makes solving common data tasks easy. A lot of precious time is usually spent on repetitive manual work such as cut & paste tasks or combining columns and applying filters. The Power Query tool makes it a whole lot easier to perform such tasks.
An added benefit here is that Power Query is easy to use when compared to other BI tools. The Power Query interface is user-friendly. Since it is very similar to the Excel interface, many users will find it comfortable.
What is Power Query?
Power Query is an application for transforming and preparing data. With Power Query you can get data from sources using a graphical interface and apply transformations using a Power Query Editor. Using Power Query, a business intelligence tool offered by Microsoft Excel, you can import data from any number of sources, clean it, transform it, then reshape it according to your needs. In this way, you can set up a query only once, re-use it later by simply refreshing.
As the name suggests, Power Query is the most powerful data automation tool found in Excel 2010 and later. Power Query allows a user to import data into Excel through external sources, such as Text files, CSV files, Web, or Excel workbooks, to list a few. The data can then be cleaned and prepared for our requirements.
Power Query has several useful features embedded in it, such as the appending of data and creating relationships between different data sets. This is called the merging of the data sets. We can also group and summarize data with the help of the tool. Needless to say, it is a very useful tool.
How Do You Enable Power Query?
Power Query is available as a free add-in on Excel 2010 and 2013, which you can download from Microsoft's website. The link is available here.
On clicking the Download button, a dialog box opens where you can choose the appropriate download option that suits your OS. Power Query will then be downloaded on your system.
It is a built-in tool starting with Excel 2016 and is available in the Get & Transforms Data Section under Data Tab.
Let’s move forward and understand the concept of Power Query.
What Can You Do With Power Query?
Power Query is a widely used ETL(Extract, Transform, Load) tool. Let’s look at the three basic steps.
1. Get Data
Importing data is easy with the help of the Get & Transform Data section of the Data tab in Excel.

You can import data from several different sources.
- From Files: Excel files(Workbook), Text or CSV files, XML files, and JSON files.
- From Databases: SQL Server, Microsoft Access, SQL Server Analysis Services.
- From Other Sources: Excel Tables/ Ranges, Web, Microsoft Query, OData feeds.

2. Transform Data
After importing the data, we can transform it with the help of Power Query. The Power Query Editor helps you transform data based on your needs.
Let’s take a look at the editor and understand its different components.
The Power Query Editor Interface

The six main sections of the Power Query Editor are as follows:
- Query Editor Ribbon: This ribbon is similar to the one on the Excel interface. Various commands are organized in separate tabs.
- Query List: This section lets you browse through a list of all queries in your current workbook.
- Formula Bar: The current transformation’s formula will be specified here in the M language.
- Data Preview: You can see the preview of your data based on the current transformation step. You can access various transformation commands by right-clicking on the column header or by clicking on the respective column header's filter option.
- Properties: This section consists of a list of query steps. Here, you will be able to name your query. Naming a query is an important step to identify a query easily.
- Applied steps: Each transformation step you take will be recorded here in chronological order. You can add, remove, edit, or reorder the steps if required.
This was all about the editor interface. Now, let’s proceed by understanding a simple transformation example on the Editor.
Follow the steps below to learn how to sort a table based on a single column.
- First, load the data onto the Editor.
- Then, select the column you want to sort.
- Click on the filter icon, as shown in the image.

- Now, you can sort the data based on Ascending or Descending order from the drop-down menu.

- On clicking OK, the table gets sorted based on the ‘Name’ column alphabetically.
You will see the M code in the formula bar. This is used to record the steps applied.

- The applied transformations will reflect in the ‘Applied Steps’ section.

Numerous other transformations can be performed on the Editor. After this step, we need to load the data onto our Excel spreadsheet.
3. Output to Excel
After performing all the operations on the editor, we will have to output it to our Excel sheet. To do this, click on the Close and Load option on the Ribbon section of the Power Query Editor.

On clicking this option, the Editor closes and loads the result to your worksheet.
In the next section, we will look at different ways by which we can Import Data to our Excel sheet.
Different Ways to Import Data to the Excel Sheet
Listed below is a detailed tutorial of importing data from various data sources.
1. Importing Data from a Text File

Follow the steps to import a text file using Power query:
- Click on the Data tab --> Text/CSV File.
- Once we have selected the “Text/CSV file” option, an ‘Import data’ dialog box is opened.
- Select the desired text file and click on Import.
- A dialog box is opened, which shows a preview of the data contained.
- Finally, click on Load to import the data.
2. Importing Data From a CSV File

You can use Power Query to import from CSV files by following the steps below:
- Click on the Data tab --> Text/CSV File.
- Once we have selected the “Text/CSV file” option, an “Import data” dialog box is opened.
- Select the desired CSV file and click on import.
- A dialog box is opened, which shows a preview of the data contained.
- Finally, click on Load to import the data.
3. Importing a Single Data Source From an Excel Workbook
To import a Single Data Source, follow these steps:
- Click on the Data tab --> Get Data command. This opens up a drop-down menu. The drop-down menu offers different options for us to import our data. To import from the Excel workbook, we select the option ‘From File’ and then ‘From Workbook’.
- Excel opens up a dialog box that helps us navigate and select the workbook.
- Once we have navigated to the workbook location, we can click on it and then click ‘Open’.
- This opens up the navigation dialog box. The navigation dialog box gives you a set of data sources.
- From here, we can select the data on which we want to work.
- Finally, click on ‘Load’ to import the data.
4. Importing a Multiple Data Source From an Excel Workbook
The following steps will help you import multiple data source from the Excel workbook:
- Click on the Data tab, followed by Get data command. On clicking this, a drop-down menu opens up. The drop-down menu offers different options for us to import our data. To import from an Excel workbook, we select the option ‘From File’ and then ‘From Workbook’.
- Excel opens up a dialog box that helps us navigate and select the workbook.
- Once we have navigated to the workbook location, we can click on it and then click ‘Open’.
- This opens up the navigation dialog box. The navigation dialog box gives you a set of data sources.
- In the navigation dialog box, there is an option to ‘Select Multiple Items’. Upon selecting this option, we can choose more than one item.
- From here, we can select the multiple data sources on which we want to work.
- Finally, click on Load to import the data.
So, these were a few techniques by which you can import data to Excel. Going ahead, let’s look at a simple demo on how you can Import Data from a CSV file.
A Demo to Get Data From CSV File
We will be explaining how to import data from a CSV file. This process is simple and consists of a few steps.
Importing Data From a CSV File
- Click on the Data tab, followed by which a Text/CSV file command is found.
- Once we have selected the “Text/CSV file” option, an ‘Import data’ dialog box is opened.

- Select the desired CSV file and click on import.

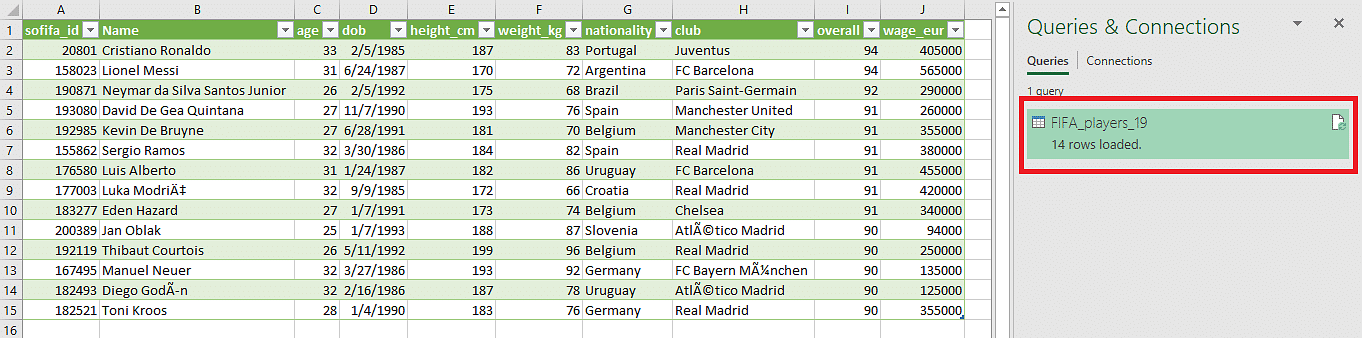
- A dialog box named after the CSV file is opened. It shows a preview of the data contained.
- Finally, click on ‘Load’ to import the data.

As you can notice, 14 rows are loaded onto the Excel sheet.
Now, let’s move forward and understand various tasks and transformations that can be performed using Power Query.
What Basic Transformations Can You Perform Using Power Query?
In this section, let’s look at various transformation functions that can be performed easily with the help of a few mouse clicks.
1. Text Formatting Functions
In this section, you will learn how to format text in Uppercase, Lowercase, and understand how to use the Trim operation.
UPPERCASE
Step 1: Load the required data onto the Power Query Editor. This can be done by selecting the respective data source from the Get & Transform Data section of the Excel Data tab. This will open up the Editor, which allows us to edit the data.
Step 2: Click on the column name and then go to the “Transform” tab, which will display a variety of options. Clicking on the option to Format text will open up a drop-down menu with a text edit option of ‘UPPERCASE’.

Step 3: Finally, on selecting the UPPERCASE edit option, all the text in the given column will be converted to uppercase.

LOWERCASE
Step 1: Load the required data onto the Power Query Editor. This can be done by selecting the respective data source from the Get & Transform Data section of the Excel data tab. This will open up the Editor, which allows us to edit the data.
Step 2: Click on the column name and then go to the ‘Transform’ tab, which will display a variety of options. Clicking on the option to Format text will open up a drop-down menu with a text edit option of ‘LOWERCASE’.

Step 3: As you can see, all the text from the selected column will be converted to lowercase.

TRIM
Step 1: Load the required data onto the Power Query Editor. This can be done by selecting the respective data source from the Get & Transform Data section of the Excel data tab. This will open up the Power Query Editor, which allows us to edit the data.
Step 2:To remove all the extra white spaces from the data, click on the column name, and then select the ‘Transform’ tab, displaying various options. Clicking on the ‘Format’ option will display a drop-down menu with a text edit option called ‘Trim’.

Step 3: Finally, on selecting the Trim edit option, all the extra white spaces in the given column will be removed.

2. Splitting a Column Using Delimiters
Step 1: Load the required data onto the Power Query Editor. This can be done by selecting the respective data source from the Get & Transform Data section of the Excel data tab. This will open up the Editor, which allows us to edit the data.
Step 2: To split the column with the help of a delimiter from the data, click on the ‘Transform’ tab followed by the ‘Split column’ option. This will display a drop-down menu with an option to split the data By Delimiter.

Step 3: A dialog box appears where you can select a delimiter. Then click on OK.

Step 4: Now, we can see that the data is split into two columns concerning the delimiter.

3. Transpose a Data Table
Step 1: Load the required data onto the Power Query Editor. This can be done by selecting the respective data source from the Get & Transform Data section of the Excel data tab. This will open up the Editor, which allows us to edit the data.
Step 2: Since we want to rotate the rows to columns, we have to navigate to the Transform tab. Upon selecting, it will show us an option to Transpose the data.

Step 3: On clicking the transpose option, the rows will be converted to columns. To load the changes into a new worksheet, go to the Home tab and click on ‘Close and load’.

4. Removing Duplicates Using Power Query
Step 1: Load the required data onto the Power Query Editor. This can be done by selecting the respective data source from the Get & Transform Data section of the Excel data tab. This will open up the Editor, which allows us to edit the data.
Look at the duplicate data highlighted in the image below.

Step 2: Now, we need to navigate to the Home tab → Remove rows option, which will open up a drop-down menu. Click on the ‘Remove Duplicates’ option.

Step 3: As you can notice, the data is now free from duplicates. To save the updated table without duplicate rows, go to the Home tab and click on ‘Close and Load’.

Combine Queries
Power Query has two different options that help us combine different datasets. The two options are:
- Append
- Merge
APPEND
In Power Query, the append operation creates a new table by joining all the rows from the first query, followed by all rows from the second query. Follow the steps below to understand how to perform an Append operation.
Step 1:
- Firstly, we have to load the data into the Excel workbook. In this demonstration, you will learn how to Append data from a CSV file.
- This can be done by selecting the Data tab, followed by the ‘Text/CSV File’ command.
- Once we have selected the option, an Import Data dialog box opens. Select the desired CSV file and click on import.
- A dialog box opens, which shows a preview of the data contained. Clicking on ‘Load’ will enter the data in a new sheet.
- Continue this step to add the required data into new sheets.
Step 2: Now, to append the data available on different sheets, we can navigate to the Data Tab. Here we can find an option called Get data, clicking on which will open up a drop-down menu. You will find an option called Combine Queries. On selecting it, you will find the ‘Append’ option.

Step 3: Clicking on ‘Append’ will open up a window with different options where we can choose to append two tables or more than three. Next, we have to select the sheets that have to be appended. When done, we can click on OK.

Step 4: The Power Query editor opens up, and the data has now been appended. We can click on ‘Close and Load’ to save these changes, which loads the updated data to an Excel spreadsheet.
MERGE
The Merge option is similar to the JOIN function in SQL. Merge is a way of combining two existing queries and creating a new query.
Step 1:
- Firstly, we have to load the data into the Excel workbook. In this example, we will demonstrate how to Merge data from a CSV file.
- This can be done by clicking on the Data tab, followed by the ‘Text/CSV File’ command.
- Once we have selected the option, an Import Data dialog box opens.
- Select the desired CSV file and click on import.
- A dialog box opens, which shows a preview of the data contained. Clicking on ‘Load’ will enter the data in a new sheet.
- Continue this step to add all the required datasets to be merged into different sheets.
Step 2: Now, to Merge the data available in different sheets, we have to navigate to the Data tab. Here we can find an option called Get Data. On clicking it, a drop-down menu will be displayed, which has the option to Combine Queries. On selecting this, click on ‘Merge’.

Step 3: A window will be displayed where we can select the sheets that we want to merge. Now, choose the two columns by clicking on the column header based on which we want to connect both the sheets. Then, click on OK.

Step 4: Once that is done, the Power Query editor opens up with a new column in the end that holds the merge result. To save the changes made, we click on “Close and Load”.
Step 5: The merged data is now loaded onto our Excel worksheet.
This was all about combining the queries using Merge and Append operations.
Kick-start your career growth story with PGP in Business Analysis. Get a chance to master Excel, Tableau, and Python tools. Start learning now!
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to load data using Power Query, perform transformations, and output the data back to your Excel worksheet. Using the Power Query tool, you are saving loads of time by performing numerous functions just with the help of a few clicks!
Whether you are interested in learning the basics of Excel or want to develop more advanced Excel skills, Simplilearn has a Business Analytics with Excel Free Course for you.
If you have any questions for us, please feel free to mention them in the comments section of this Power Query article, and we’ll have our experts answer it for you right away.
