From applying facial recognition to video streams to image classification, OpenCV is needed in more places than you think! Let us start with what is OpenCV in python.
What Is OpenCV in Python?
OpenCV python is an open-source library for machine learning, image processing, and computer vision. It plays a vital role in real-time systems, which is the key in today’s world.
How to Install OpenCV and imutils on Your System
If you do not have it already, the first step is installing OpenCV on your system. There are several installation guides available online for Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Set up a new OpenCV development environment and use pip to install the imultils package. imultis should be installed in the same environment as OpenCV using the following command:
$ pip install imutils
Use the workon command before installing imultis to enter your environment using the Python virtual environment.
Explain the OpenCV Python Project Structure
For this project, we will be using the following input image. (You can download the image and source code images from the tutorial and access them in your terminal)

To help you understand the basics of OpenCV Python, we have divided the tutorial into various sections. Follow along!
How to Load and Display an Image
In the first code block, we install cv2 and other basic libraries such as NumPy and matplotlib. Here cv2 is the OpenCV package and can be OpenCV 3 or OpenCV 4.
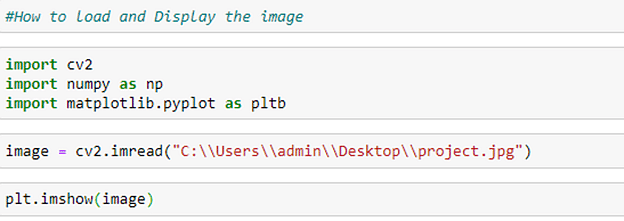
Once we have the required software, we need to load the image from the disk into memory.
We call the cv2.imread() function to load the image. Finally, we assign the result to the image variable, which is a NumPy array. The last code block prints the image. In OpenCV Python, we use the .imshow() function to display the image. The output is as follows:

How to Resize Images
Image resizing has significant importance. As there are fewer pixels to process, image processing is faster on smaller images, and we might need to resize images to fit our screen. In deep learning, images are often resized to fit into the network, which requires an image to be of a particular dimension, ignoring the aspect ratio.
Using the .resize() function, we have increased and decreased our image's size by providing changed dimensions as parameters. The image might appear to be distorted as we did not take the aspect ratio into account. Here is the output:

Increased
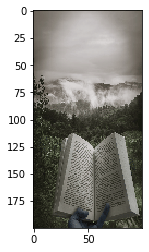
Decreased
How to Rotate Images
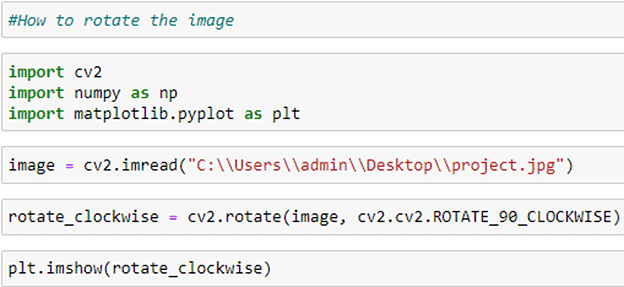
Rotating an image in OpenCV Python is fairly simple. To rotate an image about its center, we use the .rotate() function. As per requirement, the direction of rotation, that is, clockwise or anticlockwise, can be provided as a parameter shown in the source code.
The result of the given operation is:
How to Smoothen an Image
Many image processing pipelines require blurring an image in order to reduce high-frequency noise. This makes it easier for our algorithms to detect and understand the image's actual contents and not be confused by the noise. It is pretty simple to blur an image in OpenCV Python. There are several ways to carry it out, such as:
Here we use the .blur() function to perform Gaussian Blur, and we have provided the kernel as 50 x 70. The output produced is:

Small kernels yield less blurry images than larger kernels.
How to Draw On an Image
In this section, we are going to draw a line on our input image. In OpenCV Python, drawing operations are performed in place. To not destroy the original image, make a copy of the original image at the beginning of each code block.
Drawing shapes in OpenCV could not be easier. We use pre-calculated coordinates to draw a diagonal line on the image. Input these coordinates along with attributes of the shape as parameters to the .line() function. Here is the output:

How to Convert an Image to Grayscale
Similar to all other methods, we load the image into memory using the path of our image. Converting the image to grayscale is essential as we need to threshold and detect images in the upcoming sections.
We call the .cvtColor() function and use the cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY flag. We finally display the image, and here is the result:
Understanding Edge Detection
Edge detection is an effective segmentation mechanism used to find the boundaries of objects of an image.
We use the famous Canny algorithm to find the edges in the image. The following three parameters are provided to the—canny () function: input image, minimum threshold, and a maximum threshold.
Different edge maps are returned for different values of minimum and maximum thresholds such as:
What is Thresholding?
In image processing, image thresholding is a necessary intermediary step. It helps remove contours and darker or lighter regions of images.
In a single line (line 20), we grab pixels of the image and set them to black (0) corresponding to the image's background if greater than 255. For pixel values less than 120 to 255, we set it to white (foreground of the image). Here is the result:

How to Detect and Draw Contours
To detect contours, we use the .findContours() function on the grayscaled image's edge detection output. Our algorithm finds all white pixels in the image.
Then, we draw contours using the drawContours() function on the image. Here is the output:

Erosions and Dilations
Noise in binary images is a side effect of thresholding. We use the dilations and erosions to reduce this noise. To carry out this for foreground objects, we erode pixels as per the number of iterations.
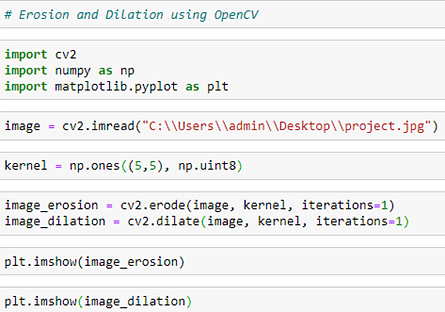
We define a NumPy array ‘kernel’ of 5X5. The number of iterations is taken as 1. For erosion, we use the .erode() function. This reduces the contour size.

For dilation, we use the .dilate() function. Here is the output:

Looking forward to making a move to the programming field? Take up the Python Training Course and begin your career as a professional Python programmer
Conclusion
This tutorial covered the basics of OpenCV Python and image processing. You can use these operations as the foundation to build an actual computer vision application. Start by creating simple object detection counters by counting contours. And in case you wish to master Python, enroll in Python Certification Training right away and scale up your programming career!

