There are many different types of project estimation techniques used in Project Management with various streams like Engineering, IT, Construction, Agriculture, Accounting, etc. A Project manager is often challenged to align mainly six project constraints - Scope, Time, Cost, Quality, Resources, and Risk in order to accurately estimate the project. The common questions that come into the mind of a project manager at the start of the project are–
- How much work is to be estimated (scope).
- How to estimate the project (techniques).
- How much time it will require to complete the project (Schedule).
- Who will be doing the project (resources)?
- What is the budget required to deliver the project (cost)?
- Any intermediary dependencies that may delay or impact the project (Risks).
We will next learn about the major parts of the project estimation techniques.
What are Project Estimation Techniques?
Project estimation techniques refer to the procedures and tools used to develop rough calculations of various aspects of any project. An excellent example of this is a project cost estimate that provides an overview of the anticipated expenses associated with the project.
Whenever stakeholders or clients require information on any project aspect, these techniques help project managers evaluate realistic numbers essential to plan a project successfully.
Why is Project Estimates Important?
Accurate estimates are critical to plan and execute a project successfully. Without precise estimates, it becomes tough to determine how long a project will take or the number of resources required.
Project managers use these estimates to ensure the team has the right people, materials, and tools available whenever needed. These estimates also help managers set realistic goals and expectations for the team members and the stakeholders.
Who Estimates Projects?
Estimating a project is typically done by the project team. Although the project manager may be in charge of the database or documents used to record estimates, the whole team and subject matter experts need to participate in creating and refining the estimates.
Engaging more knowledgeable individuals in the estimation process increases the chances of generating realistic figures. The project manager ensures the estimates are complete and updated whenever necessary.
The 3 Major Parts to Project Estimation
- Effort estimation
- Cost estimation
- Resource estimate
While accurate estimates are the basis of sound project planning, there are many techniques used as project management best practices in estimation as - Analogous estimation, Parametric estimation, Delphi method, 3 Point Estimate, Expert Judgment, Published Data Estimates, Vendor Bid Analysis, Reserve Analysis, Bottom-Up Analysis, and Simulation. Usually, during the early stages of a project life cycle, the project requirements are feebly known and less information is available to estimate the project. The initial estimate is drawn merely by assumptions knowing the scope at a high level, this is known as ‘Ball-park estimates’, a term very often used by project managers.
We will next learn about the top project estimation techniques.
Project Estimation Techniques
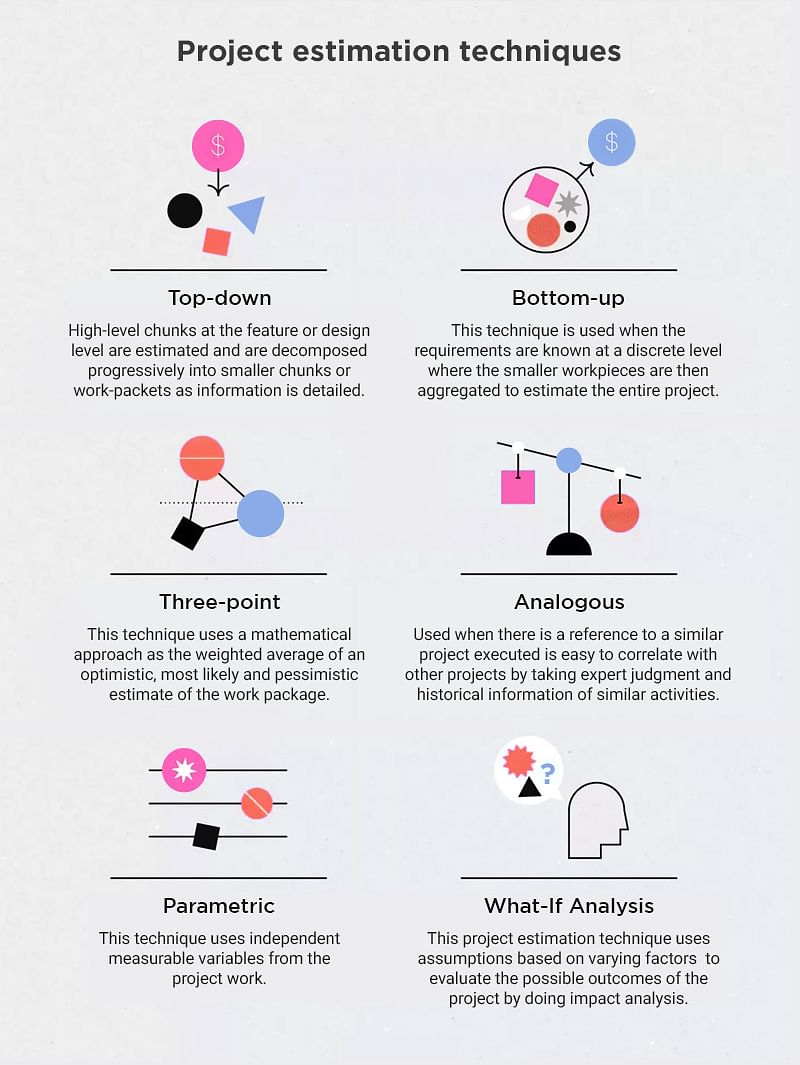
1. Top-Down Estimate
Once more detail is learned on the scope of the project, this technique is usually followed where high-level chunks at the feature or design level are estimated and are decomposed progressively into smaller chunks or work-packets as information is detailed.
2. Bottom-Up Estimate
This technique is used when the requirements are known at a discrete level where the smaller workpieces are then aggregated to estimate the entire project. This is usually used when the information is only known in smaller pieces.
3. Analogous Estimating
This project estimation technique is used when there is a reference to a similar project executed and it is easy to correlate with other projects. Expert judgment and historical information of similar activities in a referenced project are gathered to arrive at an estimate of the project.
4. Parametric Estimate
This technique uses independent measurable variables from the project work. For example, the cost for construction of a building is calculated based on the smallest variable as the cost to build a square feet area, the effort required to build a work packet is calculated from the variable as lines of codes in a software development project. This technique gives more accuracy in project estimation.
5. Three-point Estimating
This technique uses a mathematical approach as the weighted average of an optimistic, most likely and pessimistic estimate of the work package. This is often known as the PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique).
6. What-If Analysis
This project estimation technique uses assumptions based on varying factors like scope, time, cost, resources, etc., to evaluate the possible outcomes of the project by doing impact analysis. In a usual scenario, the project estimate is done by conducting estimation workshops with the stakeholders of the project, senior team members who could give valuable inputs to the estimation exercise. The high-level scope is broken down into smaller work packages, components, and activities, each work package is estimated by effort and resources needed to complete the work package. The project may be detailed into the smallest chunk that can be measured.
The following activities are done during the workshop:
- Break down the scope into smallest work package, components or activities (WBS)
- Sequence the activities in the order in which they will be performed
- Identify the effort required to complete each activity
- Identify the resource estimate to complete each task or activity
- Identify the dependencies to complete each activity
- Identify the possible risks and assumptions
- Define the resource and cost estimate to the completion of each activity, component and work package
When Should Estimates Take Place?
In a Waterfall project that follows a traditional approach, the planning phase occurs after project initiation. During this phase, estimates are made and recorded for different aspects such as scope, cost, time, resources, quality, and risks. These estimates may be subject to adjustments throughout the project as and when new information arises. For example, if new risks are identified, project risk estimates must be updated accordingly.
Agile projects, on the other hand, adopt a more iterative planning approach. Such projects are usually divided into sprints or iterations in most Agile frameworks. During the initial stage, estimates are created when compiling the overall project backlog - a list of features and requirements. During each sprint, estimates are updated either in the sprint retrospective or the sprint planning session for each new sprint.
Learn from a course that has been designed to help you ace your PMP exam in the first attemp! Check out our PMP Certification Training Course today!
Conclusion
Project estimation techniques are essential to accurately estimate several project aspects such as cost, time, scope, and more. An accurate estimate helps project managers plan and execute projects effectively while ensuring the right resources are available when necessary.
Suppose you want to learn more about the different types of project estimation techniques or gain an in-depth understanding of project management. In that case, a PMP® Certification Training course can help you learn, get certified, and apply these estimation techniques effectively. The course highlights the role of project managers while focusing on new technologies, emerging trends, and core competencies that a project manager should possess.
The above exercise gives an exact estimate of the project and the outcome of the workshop may be a project plan and a project schedule with effort, resource, and cost estimates for pmp professionals.
Happy learning! We wish you good luck with your PMP Certification Training journey!
PMBOK®, PMP®, and PMI® have registered trademarks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.

